Introduction
Cramps are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions that can affect various parts of the body, causing discomfort and pain. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods for cramps is essential, as they can disrupt daily activities and reduce productivity. This guide provides a detailed look at why cramps happen, how to manage them effectively, and tips for prevention.
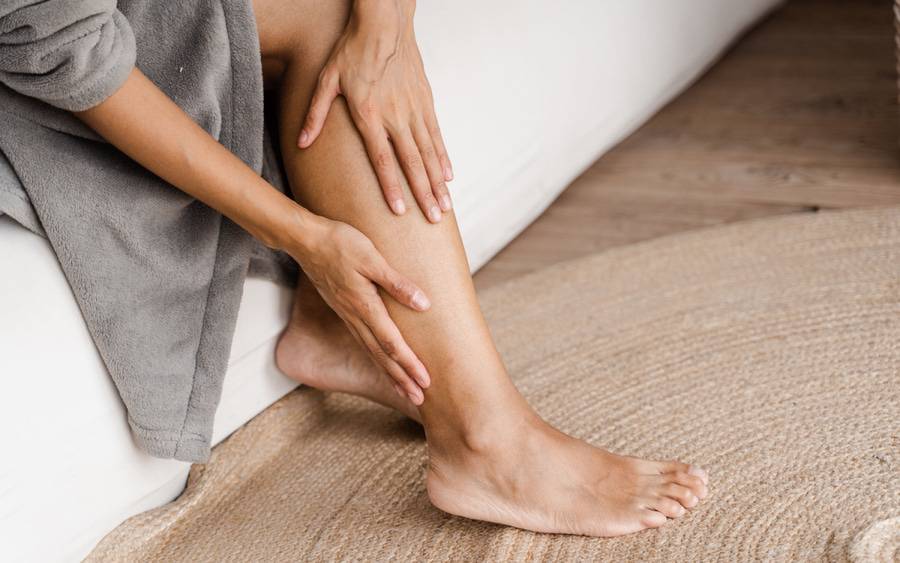

What Are Cramps?
Cramps are unexpected muscle contractions that typically last from a few seconds to several minutes. They are often experienced in the legs, but they can occur in any muscle group, including the arms, abdomen, and feet.
Common Causes of Cramps
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can cause muscle stiffness, leading to cramps.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Low levels of calcium, potassium, or magnesium are common culprits.
- Overuse of Muscles: Extended physical activity, especially without warming up, can increase the risk of cramps.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, liver disease, or thyroid issues can also contribute to frequent cramps.
Symptoms of Cramps
- Sharp, sudden muscle pain
- Muscle twitching or spasms
- Sensitivity to touch in the affected area

Effective Solutions for Cramps
-
- Hydration
Drink water throughout the day, especially if you are active or exposed to heat. Electrolyte-rich drinks can help balance minerals in the body. - Gentle Stretching
Stretch the affected area to release the contraction. For leg cramps, stretching the calf or hamstring muscles can be beneficial. - Warm Compress or Massage
Apply a warm towel or heating pad to the area and massage gently to relieve the tension. - Magnesium Supplements
Consider magnesium supplements if you experience frequent cramps. However, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice
- Hydration
Prevention Tips
- Regular Exercise: Incorporate stretching into your daily routine to keep muscles flexible.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water and consume foods high in electrolytes, such as bananas, oranges, and leafy greens.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure a diet rich in calcium, potassium, and magnesium to support muscle health.