Diabetes mellitus, often known simply as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to the hormone’s effects.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose.
Hyperglycaemia, also called raised blood glucose or raised blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body’s systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
In 2014, 8.5% of adults aged 18 years and older had diabetes. In 2019, diabetes was the direct cause of 1.5 million deaths and 48% of all deaths due to diabetes occurred before the age of 70 years. Another 460 000 kidney disease deaths were caused by diabetes, and raised blood glucose causes around 20% of cardiovascular deaths (1).
Between 2000 and 2019, there was a 3% increase in age-standardized mortality rates from diabetes. In lower-middle-income countries, the mortality rate due to diabetes increased 13%.
Causes of diabetes:
Diabetes can have a number of causes, including:
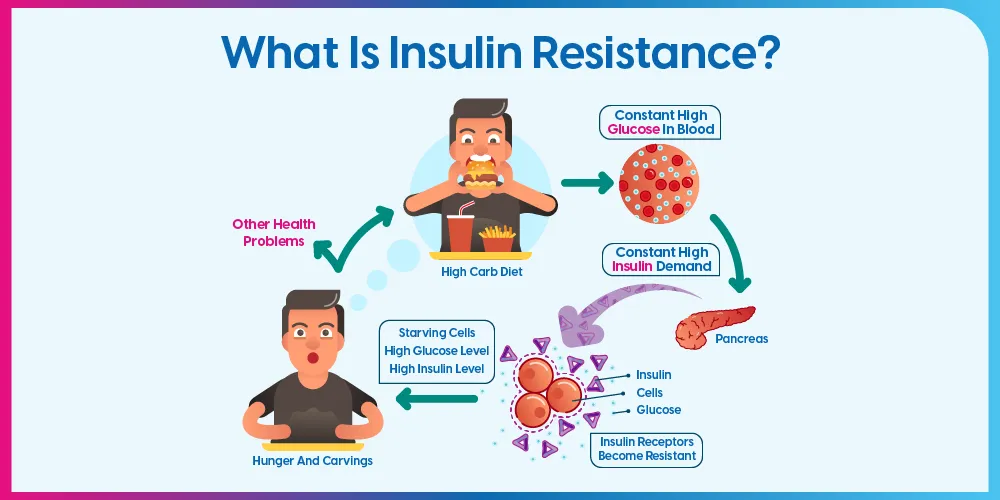
Insulin resistance:
Type 2 diabetes is often caused by insulin resistance, which occurs when cells in the body don’t respond properly to insulin. This can be due to a number of factors, including:
Weight:
Being overweight or obese can cause insulin resistance, especially if the extra weight is around the abdomen.
Diet:
Eating a lot of red meat, processed meat, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of insulin resistance.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/A-New-Study-Suggests-Eating-Processed-Meat-Can-Significantly-Increase-Your-Risk-of-Type-2-Diabetes-FT-BLOG0824-6aaad7ce303c4396a46bd7f7e53403ac.jpg)
Inactivity:
Not being physically active can increase the risk of insulin resistance.

Autoimmune disease:
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.

Genetics:
Certain genetic mutations can cause diabetes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-diabetes-genetic-5112506_final-04c9aa844032499fbcd37bc36df78b38.jpg)
Medications:
Long-term use of certain medications, such as HIV/AIDS medications and corticosteroids, can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Pancreatic damage: Physical damage to the pancreas can impact its ability to make insulin.
- Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during pregnancy, can cause insulin resistance.To prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes, you can: Maintain a healthy weight, Be physically active for at least 30 minutes a day, Eat a healthy diet, and Avoid smoking tobacco.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
Symptoms of diabetes may occur suddenly. In type 2 diabetes, the symptoms can be mild and may take many years to be noticed.
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- Feeling very thirsty
- Needing to urinate more often than usual.
- Blurred vision
- Feeling tired
- Losing weight unintentionally
Over time, diabetes can damage blood vessels in the heart, eyes, kidneys and nerves.
People with diabetes have a higher risk of health problems including heart attack, stroke and kidney failure.
Diabetes can cause permanent vision loss by damaging blood vessels in the eyes.
Many people with diabetes develop problems with their feet from nerve damage and poor blood flow. This can cause foot ulcers and may lead to amputation.
Treatment of diabetes:
Diabetes treatments include:
Insulin:
Insulin injections or an insulin pump are used to treat type 1 diabetes. Insulin is available in different forms that vary in how quickly they start working and how long they last.
Lifestyle changes:
A healthy lifestyle is one of the most important ways to treat diabetes. This includes:
- Eating healthy foods
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
Oral diabetes drugs:
Some people with type 2 diabetes need to take oral diabetes drugs to help manage their blood sugar levels. Examples include metformin, sulfonylureas, and sodium-glucose co-transporters type 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors.
Weight-loss surgery
This surgery can help people with type 2 diabetes lose weight and manage their condition. It’s generally an option for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 35 or higher.
Pancreas or islet cell transplant:
This may be an option for some people with type 1 diabetes.
Early diagnosis of diabetes is possible through inexpensive blood glucose testing.




