Depression is a mental state of low mood and aversion to activity. It affects about 3.5% of the global population, or about 280 million people of all ages (as of 2020) Depression affects a person’s thoughts, behavior, feelings, and sense of well-being. Experiences that would normally bring a person pleasure or joy give reduced pleasure or joy, and the afflicted person often experiences a loss of motivation or interest in those activities.
Depressed mood is a symptom of some mood disorders, also categorized and called depression, such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and dysthymia; it is a normal temporary reaction to life events, such as the loss of a loved one; and it is also a symptom of some physical diseases and a side effect of some drugs and medical treatments. It may feature sadness, difficulty in thinking and concentration, or a significant increase or decrease in appetite and time spent sleeping. People experiencing depression may have feelings of dejection or hopelessness, and may experience suicidal thoughts. Depression can either be short term or long term.

How it feel:
Common signs and symptoms of depression include: Persistent sad, anxious, or “empty” mood. Feelings of hopelessness or pessimism. Feelings of irritability, frustration‚ or restlessness.
Causes:
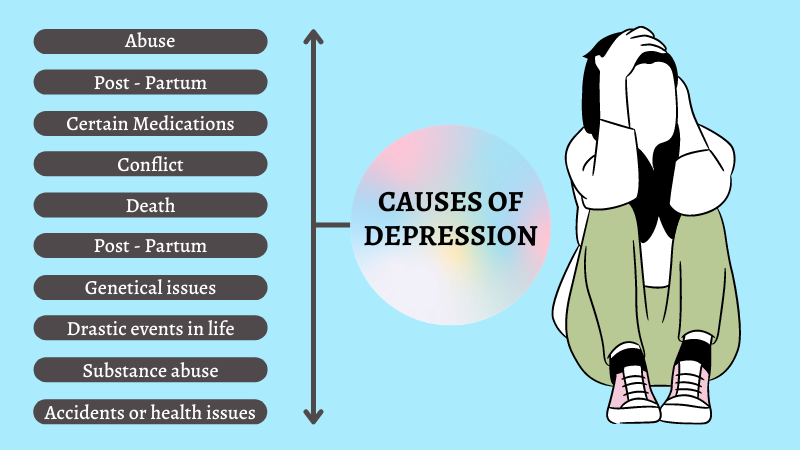
Socially stressful and traumatic life events, limited access to resources such as food, housing, and health care, and a lack of social support all contribute to depression risk.
- Stressful events. Most people take time to come to terms with stressful events, such as bereavement or a relationship breakdown. …
- Personality. …
- Family history. …
- Pregnancy and giving birth. …
- Menopause. …
- Loneliness. …
- Alcohol and drugs. …
- Illness.
- Childhood experiences.
- Life events.
- Styles of thinking.
- Other mental health problems.
- Physical health problems.
- Family history.
- Medication.
- Recreational drugs and alcohol.
How depression effect people?
Fatigue, lack of energy, or feeling slowed down. Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions. Difficulty sleeping, waking too early in the morning, or oversleeping. Changes in appetite or unplanned weight changes.
How it feels?
Common signs and symptoms of depression include: Persistent sad, anxious, or “empty” mood. Feelings of hopelessness or pessimism. Feelings of irritability, frustration‚ or restlessness.
How we fix depression?
- Stay in touch. Don’t withdraw from life. …
- Be more active. Take up some form of exercise. …
- Face your fears. Don’t avoid the things you find difficult. …
- Don’t drink too much alcohol. For some people, alcohol can become a problem. …
- Try to eat a healthy diet. …
- Have a routine.
Depression can be treated with a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes:
- Therapy: Counseling can help you find new ways to deal with your problems.
- Medication: Some types of medication that can treat depression include:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): FDA-approved MAOIs include Isocarboxazid (Marplan), Phenelzine (Nardil), and Selegiline (Emsam).
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: These drugs prevent the reabsorption of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
- Lifestyle changes: You can try these lifestyle changes to help with depression:
- Exercise: Regular exercise can improve your mood. You can start slowly with a 20-minute walk every day.
- Diet: Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet. The Mediterranean diet can improve mental health.
- Sleep: Get enough sleep. Most adults need 7–9 hours of sleep per night.
- Socializing: Stay connected with friends and family.
- Stress control: Try activities like meditation or tai chi to control stress.
- Express yourself: Do things that get your creative juices flowing, like painting, drawing, writing, or dancing.
- Notice good things: Try to notice three good things in every day.